Imagine this: you’re about to embark on a long-haul flight. Your bags are packed, your itinerary double-checked, and you’re confident you’ve thought of everything. However, upon reaching the airport security checkpoint, your precious portable charger (the lifeline for your devices during your journey) is suddenly confiscated. Why? You inadvertently violated the airline’s safety regulations. This mistake not only renders you powerless during your travels but could also result in damage to your devices. To avoid this frustrating scenario, understanding the intricate rules about carrying power banks on airplanes is crucial. In this article, we’ll unravel the complexity of these regulations to ensure your journey is both powered and smooth.
In summary, power banks are allowed on planes but must be below a specific capacity (100Wh) and can only be carried as carry-on baggage.
As usual, when it comes to airline rules and regulations, there are more details and exceptions. So, let’s take a closer look at what types of portable power sources you can bring on board.
FAA and TSA Regulations on Power Bank
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) are recognized authorities in the United States responsible for ensuring the safety and robust functionality of the aerospace system. They set the main regulations for items allowed on flights, including portable chargers or any other type of battery.
As illustrated below, you can see the primary rules for portable power sources:
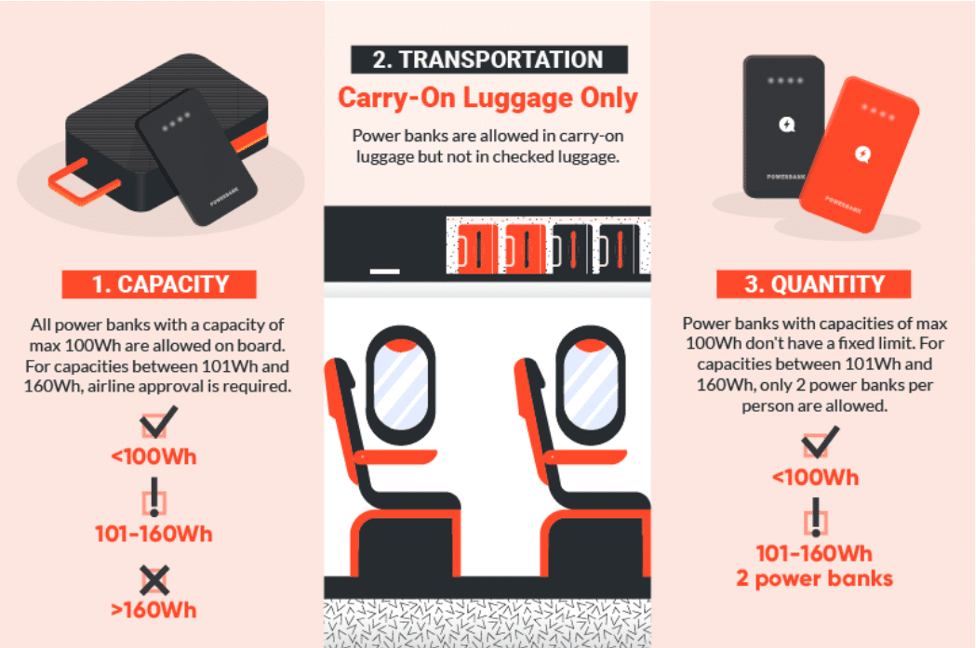
Let’s delve deeper into these rules below:
- Maximum Allowed Battery Capacity: 100Wh (or up to 160Wh with airline approval)
The FAA provides detailed guidelines on the conditions for allowing batteries on board. In principle, the capacity of any battery taken on a plane should not exceed 100Wh. They also specify that any external charger or portable power source falls under the category of batteries, and their capacity should not exceed 100Wh. This capacity is roughly equivalent to a standard power bank with 27,000mAh. Additionally, batteries with capacities between 101Wh and 160Wh require airline approval, and batteries exceeding 160Wh are strictly prohibited on planes.
- Portable Chargers and Other External Batteries Must Be in Carry-On Bags
The TSA takes a clear stance on portable chargers: these devices are only allowed in carry-on baggage and not in checked luggage. This regulation is driven by the potential risks associated with portable power sources, which may contain flammable materials, posing a fire or even explosion hazard during the flight. It’s understandable that if a fire occurs, the chances of the source being in the cabin rather than the cargo hold increase, allowing the crew a better chance to extinguish the fire.
Some passengers may be unaware of whether a portable charger is considered an independent lithium-ion battery or an integrated battery within a device. However, both the TSA and the Hazardous Materials Safety Administration describe portable chargers as “UN3480, Lithium-ion battery,” requiring specific transportation.
If you happen to place a portable charger in checked luggage, you might be asked to remove it later, or worse, airport security personnel may remove and confiscate it themselves. In either case, you wouldn’t want these situations to happen, so be sure to keep batteries in your carry-on baggage.
Proper packaging of portable batteries is also crucial to prevent potential short circuits. A effective method is to use the retail packaging. If the battery pack is missing, cover the terminals with tape, then place the battery in a box, plastic bag, or protective pouch. Ensure they won’t be accidentally activated.
- Up to Two Portable Power Sources with Capacity Between 100Wh and 160Wh
Another key factor to note is that each person is allowed to carry a maximum of two batteries with capacities between 100Wh and 160Wh on the plane. Of course, as mentioned earlier, these must have explicit approval from the airline.
TSA and FAA do not have a specific limit on the number of portable power sources below 100Wh. However, they explicitly state that all batteries must be for personal use only and transporting batteries intended for resale is not allowed.
Non-US Airlines and International Airports’ Regulations for Battery Packs
If you’re flying in Europe or Asia, the rules may differ from those in the United States. Therefore, you should check the regulations of the airline you’re flying with and the airports you’ll be passing through before flying or even booking. For example, while portable power sources with a capacity of up to 160Wh are generally allowed, some airlines may limit the maximum capacity to 100Wh.
The FAA is the regulatory body for domestic airlines in the United States, while the International Air Transport Association (IATA) is the industry association for airlines worldwide, helping to formulate industry policies and standards.
According to the document “Carriage of Lithium Batteries” released in February 2019, portable chargers fall under the category of spare batteries, and regardless of their capacity, they must be individually protected against short circuits and can only be carried as carry-on baggage. It also specifies that each passenger, without approval, may carry a maximum of 20 spare batteries of any type as long as their capacity is below or equal to 100Wh. Operators may approve the transportation of more than 20 batteries.
However, according to the 60th edition of the regulations, passengers are allowed to carry a maximum of two portable chargers with capacities between 100Wh and 160Wh, and passengers carrying chargers and batteries with capacities exceeding 160Wh must be prepared for cargo transportation under the IATA Dangerous Goods Regulations (DGR).
Pre-flight Checklist for Portable Power Sources
The following list may seem a bit daunting at first glance, but reviewing each item shouldn’t take too much time. It could potentially save your devices from being confiscated.
- Ensure your portable charger is below the 100Wh limit.
- If your device’s power is between 100Wh and 160Wh, apply for permission before the flight.
- Do not carry more than two portable chargers with capacities below 160Wh.
- Ensure your devices have a power output label.
- Place the portable charger in your carry-on baggage.
- To prevent short circuits, store spare batteries in their original packaging, a battery case, or a separate bag or pocket.
- Ensure portable chargers won’t accidentally turn on.
- Contact your airline before the flight and inquire about their restrictions.
- Check with the airports along your route and ask about their restrictions.
Why Are Portable Power Sources Regulated by the TSA?
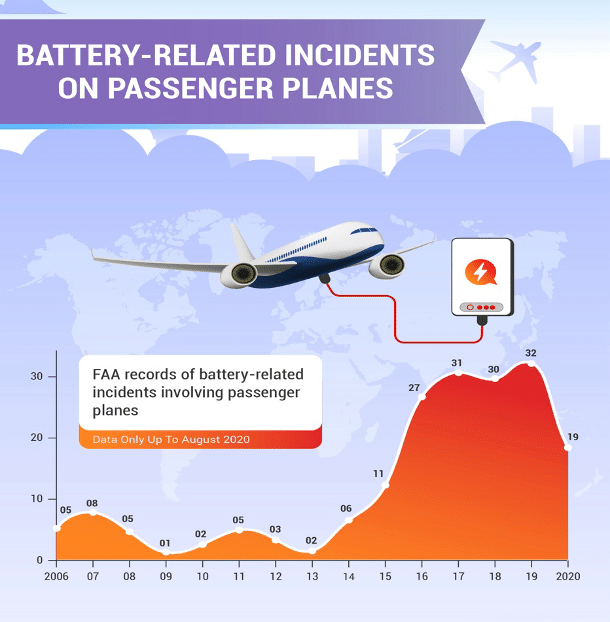
Portable power sources and other lithium-ion batteries have recently come under close scrutiny. With advances in battery technology, an increasing number of battery-powered devices are appearing on planes. However, due to their relatively unstable nature, accidents are inevitably bound to happen. After a series of battery-related incidents, some of which were quite severe, these incidents became the focus of regulations. In the graph below, you can see the evolution of battery-related incidents on aeroplanes.
To sum up,navigating air travel with portable chargers requires a keen understanding of TSA regulations to avoid unexpected inconveniences. By adhering to capacity limits, seeking airline approval for high-capacity devices, and following practical tips, travelers can ensure a seamless journey. Whether for business or leisure, a well-prepared approach to carrying portable chargers ensures that your devices stay powered, and your travel experience remains stress-free. Always stay informed, plan ahead, and enjoy the convenience of staying connected wherever your adventures take you.