In an era where our smartphones have become an indispensable part of our lives, fast-charging technology has emerged as a crucial feature. The demand for quick and efficient charging solutions led to the development of various proprietary fast-charging technologies, such as Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging, MediaTek Pump Express, and Oppo Super VOOC Flash Charge. However, one name has risen to prominence as the leading and most widely used fast-charging technology: Qualcomm Quick Charge. This article delves into what Qualcomm Quick Charge is, how it works, and why it has become a cornerstone of the modern charging landscape.
What is Qualcomm Quick Charge Technology?
Qualcomm Quick Charge, introduced by the Qualcomm corporation in 2013, revolutionized the fast-charging game. It offers higher power delivery compared to the traditional 5 Volts / 2 Amps USB charging rate. This enhanced power delivery enables compatible devices to charge faster, reducing the time users need to spend tethered to power outlets.
Why is Qualcomm Quick Charge So Popular?
The popularity of Qualcomm Quick Charge can be attributed to three key factors: Connector and Current Independence:
Qualcomm Quick Charge is designed to be connector and current independent. It is compatible with a wide range of ports, including USB type A, USB type C, and micro USB, covering the majority of Android smartphones. This compatibility simplifies the charging experience for users.
High-Voltage Operation:
Quick Charge operates with high-voltage, which mitigates charging issues related to cable length and thickness. Users can expect an optimal charging experience regardless of the cable type or its current capability.
High Power Delivery:
In a world where most modern smartphones can be charged with 18 Watts of power, Qualcomm Quick Charge is up to the task. In fact, Quick Charge has evolved to provide up to 100 Watts of power, making it suitable for various devices beyond smartphones.
Versions of Qualcomm Quick Charge
As smartphone manufacturers continue to compete by offering devices with larger battery capacities, the development of Quick Charge technology keeps pace. Currently, there are five versions of Qualcomm Quick Charge: Quick Charge 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and the latest iteration, Quick Charge 4+. Each new version has brought enhancements and optimizations, with Quick Charge 2.0 and 3.0 being the most prevalent in current smartphones.
Importantly, Qualcomm Quick Charge is backward compatible, meaning that a charger with Quick Charge 3.0 can work seamlessly with a smartphone equipped with Quick Charge 2.0, ensuring versatility and convenience for users. To provide a better understanding of the evolution of Qualcomm Quick Charge, let’s take a closer look at the key features and improvements introduced in each generation:
- Qualcomm Quick Charge 1.0
The first version of Qualcomm Quick Charge was introduced in 2013, and soon made a big splash thanks to the fact that it supplies 5 Volts and draws a current of 2 A, maximizing charging efficiency to 10 watts of power. While nowadays, it’s considered “normal charging”, it was groundbreaking back in the day.
- Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0
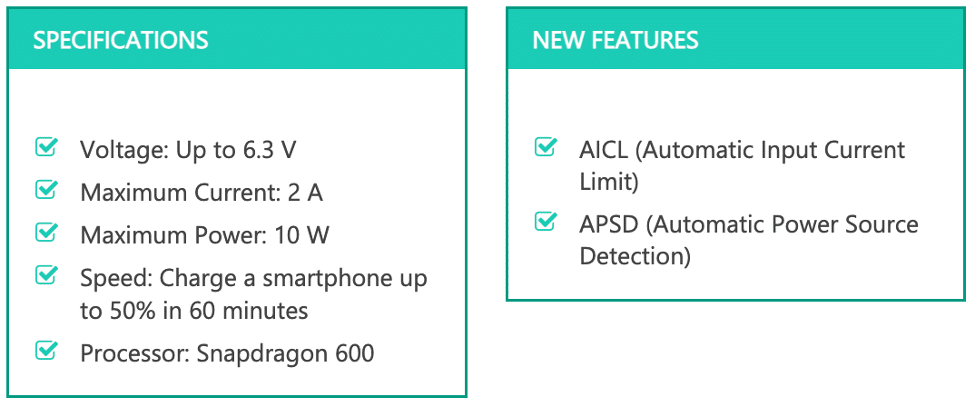
A year after the introduction of Quick Charge 1.0, Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0 came. One of the most notable features is that it allows a higher voltage supply and a maximum current of 3A. While the maximum voltage of Class A is 12 Volts, Class B chargers supply up to 20 Volts, which is great to charge not only smartphones but also tablets and laptops. Besides, another improvement is its compatibility with a wide array of processors, unlike the previous version.
- Qualcomm Quick Charge 3.0
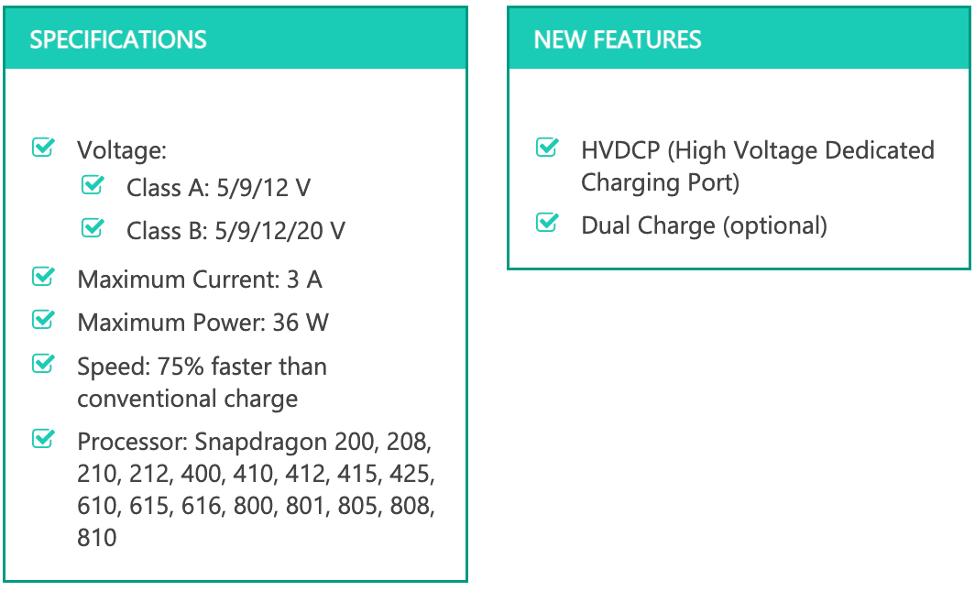
Quick Charge 3.0 was announced in late 2015 and released in early 2016. Implementing the Intelligent Negotiation for Optimum Voltage (INOV), QC3.0 is able to transfer optimum power by determining the voltage level necessary throughout time. This is why QC3.0 works with voltage levels ranging from 3.6 V to 20 V, with increments of 200 mV. The result is a faster and more efficient charge than Quick Charge 2.0, being capable of powering a 2750mAh battery up to 80% in 35 minutes.
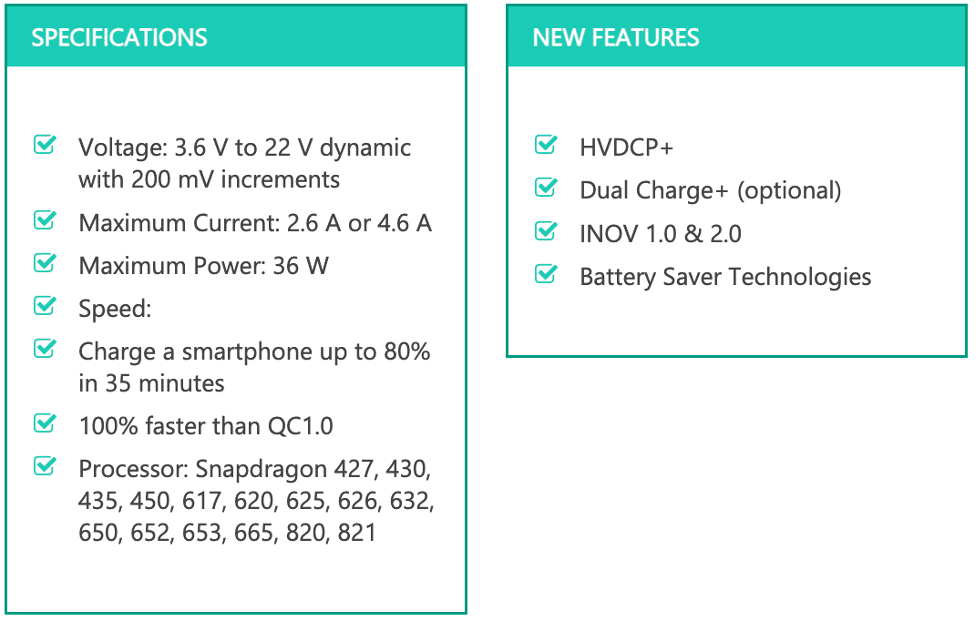
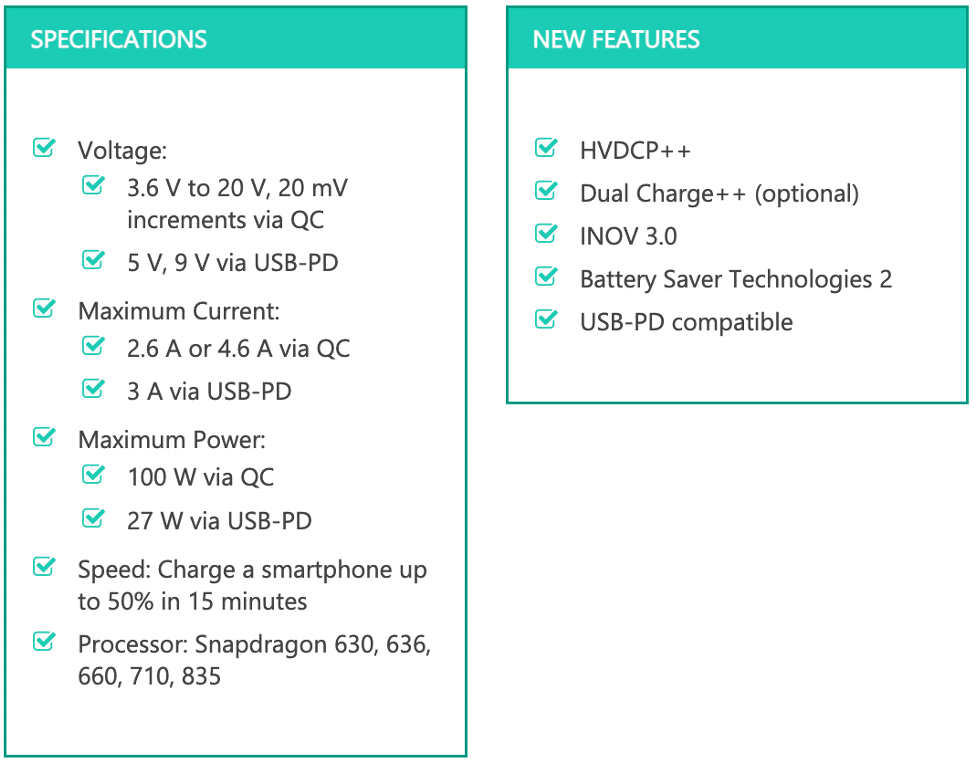
- Qualcomm Quick Charge 4.0
Quick Charge 4.0 was announced in December 2016 and released to the market in the first half of the following year. It is 20% faster and 30% more efficient than Quick Charge 3.0, keeping its temperature about 5°C cooler. However, its premiere feature is that it is USB-C USB-PD (Power Delivery) compliant, and it also includes safety measures to protect devices and the unit itself against charging problems, such as overheating, over-voltage and over-current.
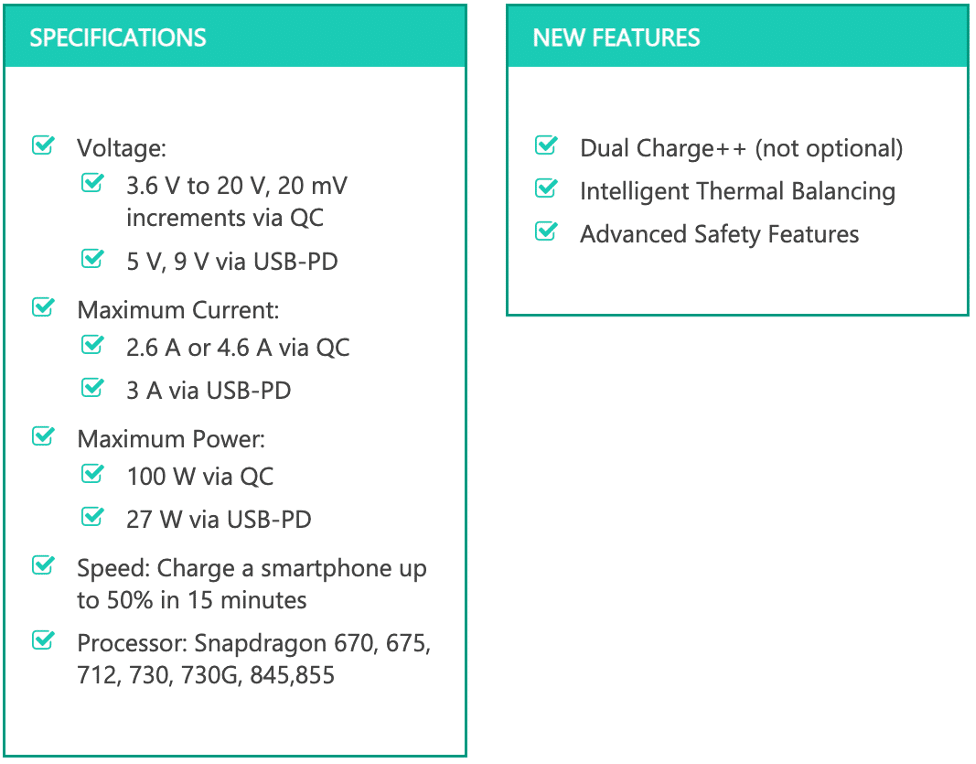
- Qualcomm Quick Charge 4+
Quick Charge 4+ was announced on June 1, 2017. This improved version of Quick Charge 4.0 features Intelligent Thermal Balancing and Advanced Safety Features to eliminate hot spots and protect against overheating and short-circuit or damage of the USB-C connector. Besides, Dual Charge++ is required, whereas in prior versions Dual Charge was optional. Lastly, Qualcomm claims that compared to its predecessor, this version is 15% faster, and charges up to 30% more efficiently while operating 3°C cooler.
Qualcomm VS Power Delivery (PD)
Two prominent contenders in the fast-charging arena are Qualcomm Quick Charge and Power Delivery (PD), both aiming to provide users with quick and convenient power-up options.
Understanding Power Delivery (PD): Power Delivery, often referred to as PD, is a standard protocol established by the USB-IF standards organization. It can deliver up to 100W of power at 20V and 5A, making it a preferred choice for devices with substantial power requirements, such as tablets and laptops. PD is commonly associated with USB Type-C ports, which have become more prevalent in modern devices.
Google Pixel phones are equipped with USB Type-C ports and iPhones have USB-C ports from the 15th generation.
Which one is faster?
When it comes to speed, there isn’t a substantial difference between Qualcomm Quick Charge and Power Delivery. The true differentiators lie in other factors, such as versatility, cost, and use.
Qualcomm Quick Charge 4.0 and 4+ are designed to deliver up to 27W of power, making them compatible with Power Delivery. Most smartphones typically require around 18W for charging, which is why Qualcomm Quick Charge has garnered widespread support from smartphone manufacturers.
In the grand scheme of things, Power Delivery offers enough power to charge a range of devices, from smartphones to laptops. However, Qualcomm Quick Charge 4.0 and 4+ integrate Power Delivery and are compatible with a broader range of USB connectors, making them an excellent choice for users who value versatility and wish to save money. If your goal is to charge all your PD/USB-C compatible devices, including laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles like the Nintendo Switch, a single PD charger can fulfill all your needs.
Final Thoughts
Qualcomm Quick Charge has undeniably revolutionized the way we charge our devices, enabling fast-speed charging that is now embraced by almost every brand worldwide. This technology provides an array of compatible USB ports, USB-powered devices, chargers, and power banks, allowing users to stay connected without being tethered to power outlets for extended periods.
While today’s charging speeds are impressive, the future undoubtedly holds further advancements. One thing is certain: Qualcomm Quick Charge will continue evolving and optimizing the charging process, keeping pace with the ever-increasing demands of the digital age. As consumers, we can anticipate even faster, more efficient, and more convenient charging solutions on the horizon, thanks to the relentless pursuit of innovation in the field of fast-charging technology.